Source Website: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_index
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, last edited on 22 December 2016, at 03:18
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, last edited on 22 December 2016, at 03:18
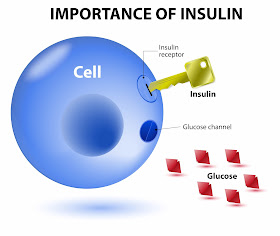
PHOTO: Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows our body to use sugar (glucose) from carbohydrates in the food that we eat for energy or to store glucose for future use. Insulin helps keeps our blood sugar level from getting too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia).
Picture posted by Personal Training Master on 24 September 2016
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg52X7ooa_dhZGmxUzaotninhbCxD-rQco_4hTgF176VJWrqqVK605WkOWGzupfBk9w_PhLG0YjLJvmvrmbyepaC5CrAoCz4VTZ2axoC0scHPiZsF3g0BpMg-DlnPTS3ZUnYSAJM_w3jDU/s1600/Insulin+receptors-min.jpg
https://www.personaltrainingmaster.co.uk/sites/default/files/Insulin%20receptors-min.jpg
https://www.personaltrainingmaster.co.uk/what-food-and-exercise-helps-diabetes-guidelines-and-high-intensity-exercise-effects-part-4
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows our body to use sugar (glucose) from carbohydrates in the food that we eat for energy or to store glucose for future use. Insulin helps keeps our blood sugar level from getting too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia).
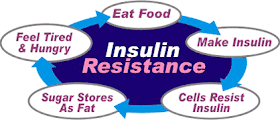
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin. ... When the body produces insulin under conditions of insulin resistance, the cells are resistant to the insulin and are unable to use it as effectively, leading to high blood sugar.
Picture posted by Personal Training Master on 24 September 2016
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg52X7ooa_dhZGmxUzaotninhbCxD-rQco_4hTgF176VJWrqqVK605WkOWGzupfBk9w_PhLG0YjLJvmvrmbyepaC5CrAoCz4VTZ2axoC0scHPiZsF3g0BpMg-DlnPTS3ZUnYSAJM_w3jDU/s1600/Insulin+receptors-min.jpg
https://www.personaltrainingmaster.co.uk/sites/default/files/Insulin%20receptors-min.jpg
https://www.personaltrainingmaster.co.uk/what-food-and-exercise-helps-diabetes-guidelines-and-high-intensity-exercise-effects-part-4
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows our body to use sugar (glucose) from carbohydrates in the food that we eat for energy or to store glucose for future use. Insulin helps keeps our blood sugar level from getting too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia).
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin. ... When the body produces insulin under conditions of insulin resistance, the cells are resistant to the insulin and are unable to use it as effectively, leading to high blood sugar.
PHOTO: When sugar is in the blood, INSULIN is around. When insulin is around, our fat burning abilities go on hold! So the MORE INSULIN we have in our blood, the HARDER IT IS TO BURN FAT.
So if we eat less sugar, our insulin levels will remain LOW and our body is able to access its fat stores to BURN.
If insulin is around too often in high quantities (as a result of eating refined carbohydrates and added sugars), cells can become resistant to it and more and more insulin is required to get the glucose inside the cells.
This insulin resistance is the leading driver of many diseases including obesity, cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Picture posted by Rebecca Miller - Nutritionist and Director of Health with Bec on 05 May 2016
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhh7y9dndu1LY9GpLtDiuE6WpjgGatvnrdQtn9vB2M0L36li0PPQojdmA3u_s0J-I8j8suLxHIatjl0T0TtdqaB5aV5noO9B5D1ntauSFtkmrlum1g3scy2WQSuRGpprI2lTpp96AZ5fPg/s1600/static1.squarespace.com.png
https://static1.squarespace.com/static/56dfbe851bbee0d08ab190ff/t/5729b835746fb96357bfc773/1462351934670/?format=500w
http://www.healthwithbec.com/blog/2016/4/28/what-does-sugar-actually-do-to-our-bodies
If our blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be considered type 2 diabetes, we have a condition called prediabetes. It's not entirely clear why some people develop insulin resistance and others don't. Being overweight or obese are the leading risk factors.
The Insulin Index of a food represents how much it elevates the concentration of insulin in the blood during the two-hour period after the food is ingested. The index is similar to the Glycemic Index (GI) and Glycemic Load (GL), but rather than relying on blood glucose levels, the Insulin Index is based upon blood insulin levels. The Insulin Index represents a comparison of food portions with equal overall caloric content (250 kcal or 1000 kJ), while GI represents a comparison of portions with equal digestible carbohydrate content (typically 50 g) and the GL represents portions of a typical serving size for various foods. The Insulin Index can be more useful than either the Glycemic Index or the Glycemic Load because certain foods (e.g., lean meats and proteins) cause an insulin response despite there being no carbohydrates present, and some foods cause a disproportionate insulin response relative to their carbohydrate load.
So if we eat less sugar, our insulin levels will remain LOW and our body is able to access its fat stores to BURN.
If insulin is around too often in high quantities (as a result of eating refined carbohydrates and added sugars), cells can become resistant to it and more and more insulin is required to get the glucose inside the cells.
This insulin resistance is the leading driver of many diseases including obesity, cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
Picture posted by Rebecca Miller - Nutritionist and Director of Health with Bec on 05 May 2016
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhh7y9dndu1LY9GpLtDiuE6WpjgGatvnrdQtn9vB2M0L36li0PPQojdmA3u_s0J-I8j8suLxHIatjl0T0TtdqaB5aV5noO9B5D1ntauSFtkmrlum1g3scy2WQSuRGpprI2lTpp96AZ5fPg/s1600/static1.squarespace.com.png
https://static1.squarespace.com/static/56dfbe851bbee0d08ab190ff/t/5729b835746fb96357bfc773/1462351934670/?format=500w
http://www.healthwithbec.com/blog/2016/4/28/what-does-sugar-actually-do-to-our-bodies
If our blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be considered type 2 diabetes, we have a condition called prediabetes. It's not entirely clear why some people develop insulin resistance and others don't. Being overweight or obese are the leading risk factors.
The Insulin Index of a food represents how much it elevates the concentration of insulin in the blood during the two-hour period after the food is ingested. The index is similar to the Glycemic Index (GI) and Glycemic Load (GL), but rather than relying on blood glucose levels, the Insulin Index is based upon blood insulin levels. The Insulin Index represents a comparison of food portions with equal overall caloric content (250 kcal or 1000 kJ), while GI represents a comparison of portions with equal digestible carbohydrate content (typically 50 g) and the GL represents portions of a typical serving size for various foods. The Insulin Index can be more useful than either the Glycemic Index or the Glycemic Load because certain foods (e.g., lean meats and proteins) cause an insulin response despite there being no carbohydrates present, and some foods cause a disproportionate insulin response relative to their carbohydrate load.
PHOTO: GI represents a comparison of portions with equal digestible carbohydrate content (typically 50 g) and the GL represents portions of a typical serving size for various foods. The Insulin Index can be more useful than either the Glycemic Index or the Glycemic Load because certain foods (e.g., lean meats and proteins) cause an insulin response despite there being no carbohydrates present, and some foods cause a disproportionate insulin response relative to their carbohydrate load.
Picture posted by Amy White MS HNC, holistic nutrition counselor on 11 July 2016
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgDDrnZaYqgf1bpOUb8gESxk-SkLQItEigwfktpi7T0NMvb2GbY-nOO4nXNO7ZSOCxmV_dQvTRBAvBYqVNlDBWTLumAr6WlXaU0e7Nvwr-ZR00fDTMvFuUk2O053XZVPdgMT9F48eSAxjs/s1600/Screen-Shot-2016-07-10-at-5.37.23-PM.png
http://simplicityofwellness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/Screen-Shot-2016-07-10-at-5.37.23-PM.png
http://simplicityofwellness.com/2016/07/insulin/
Holt et al.[1] have noted that the glucose and insulin scores of most foods are highly correlated,[2] but high-protein foods and bakery products that are rich in fat and refined carbohydrates "elicit insulin responses that were disproportionately higher than their glycemic responses." They also conclude that insulin indices may be useful for dietary management and avoidance of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia.
Explanation of Index
The Insulin Index is not the same as a glycemic index (GI), which is based exclusively on the digestible carbohydrate content of a food, and represents a comparison of foods in amounts with equal digestible
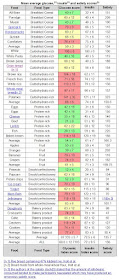
carbohydrate content (typically 50 g). The insulin index compares foods in amounts with equal overall caloric content (250 kcal or 1000 kJ). Insulin indexes are scaled relative to white bread, while glycemic index scores nowadays are usually scaled with respect to pure glucose, although in the past white bread has been a reference point for GI measurements as well. In the chart below, glycemic and insulin scores show the increase in the blood concentration of each. A higher satiety score indicates how much less was eaten from a buffet after participants ate the listed food.
Picture posted by Amy White MS HNC, holistic nutrition counselor on 11 July 2016
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgDDrnZaYqgf1bpOUb8gESxk-SkLQItEigwfktpi7T0NMvb2GbY-nOO4nXNO7ZSOCxmV_dQvTRBAvBYqVNlDBWTLumAr6WlXaU0e7Nvwr-ZR00fDTMvFuUk2O053XZVPdgMT9F48eSAxjs/s1600/Screen-Shot-2016-07-10-at-5.37.23-PM.png
http://simplicityofwellness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/Screen-Shot-2016-07-10-at-5.37.23-PM.png
http://simplicityofwellness.com/2016/07/insulin/
Holt et al.[1] have noted that the glucose and insulin scores of most foods are highly correlated,[2] but high-protein foods and bakery products that are rich in fat and refined carbohydrates "elicit insulin responses that were disproportionately higher than their glycemic responses." They also conclude that insulin indices may be useful for dietary management and avoidance of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia.
Explanation of Index
The Insulin Index is not the same as a glycemic index (GI), which is based exclusively on the digestible carbohydrate content of a food, and represents a comparison of foods in amounts with equal digestible
carbohydrate content (typically 50 g). The insulin index compares foods in amounts with equal overall caloric content (250 kcal or 1000 kJ). Insulin indexes are scaled relative to white bread, while glycemic index scores nowadays are usually scaled with respect to pure glucose, although in the past white bread has been a reference point for GI measurements as well. In the chart below, glycemic and insulin scores show the increase in the blood concentration of each. A higher satiety score indicates how much less was eaten from a buffet after participants ate the listed food.
PHOTO: Mean average glucose, insulin and satiety scores
[n 1] Rye bread containing 47% kibbled rye, Holt et al
[n 2] Bread made from whole-meal wheat flour, Holt et al, .
[n 3] the authors of the satiety study[3] stated that the amount of jellybeans consumed tended to make participants nauseated which may have produced an erroneous satiety score.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, last edited on 22 December 2016, at 03:18
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiGWCmx_HK5XtRcSW_riGXtvg85bKx3ogryebEc8rRRCLiQhijhmHg242ir2vYjx3nbLfB2SiDb6K9HDQuPo-PWZ56zF4ssOKeuCFtJW7AXn-fZ6_XLOC5oBnNaOQA-iEPzIioSrEGE2KU/s1600/Insulin+index.jpg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_index
Glucose (glycemic) and insulin scores were determined by feeding 1000 kilojoules (239 kilocalories) of the food to the participants and recording the area under the glucose/insulin curve for 120 minutes then dividing by the area under the glucose/insulin curve for white bread. The result being that all scores are relative to white bread. The satiety score was determined by comparing how satiated participants felt within two hours after being fed a fixed number of calories (240 kilocalories) of a particular food while blindfolded (to ensure food appearance was not a factor), then dividing that number by how satiated the participants felt after eating white bread. White bread serves as the baseline of 100. In other words, foods scoring higher than 100 are more satisfying than white bread and those under 100 are less satisfying. The satiety score was negatively correlated to the amount eaten by participants at a subsequent buffet.
± indicate uncertainty in the data. For example 60 ± 12 means that there's a 95% chance the score is between 60-12 (48) and 60+12 (72), 60 being the highest probability assuming a bell curve. In practice this means that if two foods have large uncertainty and have values close together then you don't really know which score is the higher.
[2] Cousens, Gabriel (2008). There Is a Cure for Diabetes: The Tree of Life 21-Day+ Program. North Atlantic Books. p. 144. ISBN 978-1-55643-691-8.
[3] Holt, Susanne H.A.; Brand-Miller, Janette Cecile; Petocz, Peter; Farmakalidis, E. (September 1995). "A satiety index of common foods". European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 49 (9): 675–690. PMID 7498104. Lay summary – The Satiety Index — What Really Satisfies (2005-01-10).
Mäkeläinen H, Anttila H, Sihvonen J, et al. (June 2007). "The effect of β-glucan on the glycemic and insulin index". Eur J Clin Nutr. 61 (6): 779–85. PMID 17151593. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602561.
[n 1] Rye bread containing 47% kibbled rye, Holt et al
[n 2] Bread made from whole-meal wheat flour, Holt et al, .
[n 3] the authors of the satiety study[3] stated that the amount of jellybeans consumed tended to make participants nauseated which may have produced an erroneous satiety score.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, last edited on 22 December 2016, at 03:18
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiGWCmx_HK5XtRcSW_riGXtvg85bKx3ogryebEc8rRRCLiQhijhmHg242ir2vYjx3nbLfB2SiDb6K9HDQuPo-PWZ56zF4ssOKeuCFtJW7AXn-fZ6_XLOC5oBnNaOQA-iEPzIioSrEGE2KU/s1600/Insulin+index.jpg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_index
Glucose (glycemic) and insulin scores were determined by feeding 1000 kilojoules (239 kilocalories) of the food to the participants and recording the area under the glucose/insulin curve for 120 minutes then dividing by the area under the glucose/insulin curve for white bread. The result being that all scores are relative to white bread. The satiety score was determined by comparing how satiated participants felt within two hours after being fed a fixed number of calories (240 kilocalories) of a particular food while blindfolded (to ensure food appearance was not a factor), then dividing that number by how satiated the participants felt after eating white bread. White bread serves as the baseline of 100. In other words, foods scoring higher than 100 are more satisfying than white bread and those under 100 are less satisfying. The satiety score was negatively correlated to the amount eaten by participants at a subsequent buffet.
± indicate uncertainty in the data. For example 60 ± 12 means that there's a 95% chance the score is between 60-12 (48) and 60+12 (72), 60 being the highest probability assuming a bell curve. In practice this means that if two foods have large uncertainty and have values close together then you don't really know which score is the higher.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, last edited on 22 December 2016, at 03:18
Reference
[1] Holt, Susanne H.A.; Brand-Miller, Janette Cecile; Petocz, Peter (November 1997). "An insulin index of foods: the insulin demand generated by 1000-kJ portions of common foods" (PDF). American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 66 (5): 1264–76. PMID 9356547. Lay summary – Insulin Index (2009-10-14).[2] Cousens, Gabriel (2008). There Is a Cure for Diabetes: The Tree of Life 21-Day+ Program. North Atlantic Books. p. 144. ISBN 978-1-55643-691-8.
[3] Holt, Susanne H.A.; Brand-Miller, Janette Cecile; Petocz, Peter; Farmakalidis, E. (September 1995). "A satiety index of common foods". European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 49 (9): 675–690. PMID 7498104. Lay summary – The Satiety Index — What Really Satisfies (2005-01-10).
Mäkeläinen H, Anttila H, Sihvonen J, et al. (June 2007). "The effect of β-glucan on the glycemic and insulin index". Eur J Clin Nutr. 61 (6): 779–85. PMID 17151593. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602561.
- https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg52X7ooa_dhZGmxUzaotninhbCxD-rQco_4hTgF176VJWrqqVK605WkOWGzupfBk9w_PhLG0YjLJvmvrmbyepaC5CrAoCz4VTZ2axoC0scHPiZsF3g0BpMg-DlnPTS3ZUnYSAJM_w3jDU/s1600/Insulin+receptors-min.jpg
- https://www.personaltrainingmaster.co.uk/sites/default/files/Insulin%20receptors-min.jpg
- https://www.personaltrainingmaster.co.uk/what-food-and-exercise-helps-diabetes-guidelines-and-high-intensity-exercise-effects-part-4
- https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhh7y9dndu1LY9GpLtDiuE6WpjgGatvnrdQtn9vB2M0L36li0PPQojdmA3u_s0J-I8j8suLxHIatjl0T0TtdqaB5aV5noO9B5D1ntauSFtkmrlum1g3scy2WQSuRGpprI2lTpp96AZ5fPg/s1600/static1.squarespace.com.png
- https://static1.squarespace.com/static/56dfbe851bbee0d08ab190ff/t/5729b835746fb96357bfc773/1462351934670/?format=500w
- http://www.healthwithbec.com/blog/2016/4/28/what-does-sugar-actually-do-to-our-bodies
- https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgDDrnZaYqgf1bpOUb8gESxk-SkLQItEigwfktpi7T0NMvb2GbY-nOO4nXNO7ZSOCxmV_dQvTRBAvBYqVNlDBWTLumAr6WlXaU0e7Nvwr-ZR00fDTMvFuUk2O053XZVPdgMT9F48eSAxjs/s1600/Screen-Shot-2016-07-10-at-5.37.23-PM.png
- http://simplicityofwellness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/Screen-Shot-2016-07-10-at-5.37.23-PM.png
- http://simplicityofwellness.com/2016/07/insulin/